Investment Thesis: Coupang

Coupang, Inc. is a U.S.-based technology company and Fortune 150 enterprise redefining how commerce operates at scale. Often described as “the Amazon of South Korea,” Coupang has built a deeply integrated logistics and technology platform centered on one core principle: delivering the best customer experience on the planet. Through relentless execution, proprietary fulfillment infrastructure, and continuous innovation, Coupang has transformed everyday commerce into a faster, more reliable, and increasingly global ecosystem. This investment thesis examines whether Coupang’s customer-obsessed model and expanding platform can translate operational excellence into durable long-term shareholder value.
This recommendation is just a start. The next step is to do your due diligence process, which will then help you make the investment decision. We strongly advise investors to do a thorough analysis of the recommendation and understand the soundness of the business before investing in this company. Also, please consult your investment advisor before making a decision.
Business Profile (NYSE: CPNG)
Coupang, Inc. operates at the intersection of e-commerce, logistics, and technology, with a business model built to remove friction from everyday life.
It is a technology-driven commerce platform offering a wide range of products and services, including first-party and third-party retail, food delivery, video streaming, and fintech-adjacent services. Its defining feature is speed and reliability, enabled by an end-to-end logistics network that Coupang owns and operates. This vertical integration allows the company to control inventory, fulfillment, and last-mile delivery at scale. It primarily serves consumers seeking convenience, value, and reliability, ranging from everyday households to time-constrained urban professionals. On the supply side, Coupang supports merchants and brands by providing access to a massive customer base, logistics infrastructure, and data-driven tools that lower barriers to selling online.
Coupang’s core operations are based in South Korea, one of the world’s most densely populated and digitally connected markets. The company has also expanded into adjacent geographies and services, using its Korean operations as a proving ground before scaling selectively. Its competitive edge lies in its obsessive focus on customer experience. Features like next-day or same-day delivery, dawn delivery, frictionless returns, and transparent pricing create high customer trust and habitual usage. Rather than optimizing for short-term margins, Coupang prioritizes long-term engagement, retention, and ecosystem depth.
Revenue is generated through product sales, third-party marketplace fees, logistics and fulfillment services, subscriptions, advertising, and adjacent digital offerings. As scale increases, Coupang benefits from operating leverage in logistics, data, and technology, allowing fixed infrastructure costs to be spread across a growing transaction base. Coupang’s execution is driven by continuous reinvestment in technology, automation, and infrastructure. Its software-defined logistics system, combined with data-driven decision-making, enables rapid iteration and operational improvements. This tight integration between tech and physical operations is central to Coupang’s ability to innovate faster than traditional retailers.
Coupang functions less like a conventional retailer and more like a commerce infrastructure platform, designed to compound customer value over time while building durable competitive advantages.
Story
Coupang, Inc. was founded in 2010 by Bom Kim, a South Korea–born entrepreneur educated in the United States, with a simple but ambitious idea: commerce should save people time. What followed was not a straight path but a series of deliberate bets that reshaped how commerce works in South Korea and beyond.
2010 to 2013: The Experimentation Phase
Coupang began as a group-buying and daily deals platform, similar to early social commerce models. Growth came quickly, but so did friction. The real bottleneck was not demand or pricing, but delivery. Customers wanted reliability and speed, and the existing logistics ecosystem could not deliver either.
2014 to 2018: The Logistics Bet
Instead of outsourcing fulfillment, Coupang chose to build its own logistics network from scratch. Warehouses, software systems, and last-mile delivery were brought in-house. This period marked Coupang’s shift from a marketplace to an integrated commerce platform. Rocket Delivery emerged, making next-day delivery the baseline rather than a premium service.
2019 to 2020: Customer Experience as Strategy
Coupang expanded beyond speed into convenience. Dawn delivery, doorstep returns with no packaging required, and highly transparent pricing turned logistics into a competitive moat. Heavy reinvestment drew skepticism, but Coupang treated this phase as infrastructure construction rather than short-term profit optimization.
2021: Global Capital, Long-Term Vision
Coupang’s U.S. IPO provided long-term capital and reinforced its positioning as a technology company. The listing was not an endpoint but a funding milestone that enabled further ecosystem expansion.
2022 to 2026: Platform Expansion and Maturity
Coupang layered in new services such as food delivery, streaming, and merchant tools, increasing customer engagement and lifetime value. Its logistics and data systems became more automated and efficient, improving unit economics while maintaining service quality.
Impact and Innovation
Coupang is no longer just an online retailer. It has reset consumer expectations around delivery speed, reliability, and returns; influenced labor models in last-mile logistics; and demonstrated how long-term customer obsession can translate into durable competitive advantage. What started as a deals site is now a foundational piece of commerce infrastructure, quietly embedded in everyday life.
Business Model
Coupang, Inc. operates a vertically integrated commerce model designed to maximize convenience, reliability, and long-term customer value. Rather than acting purely as a marketplace, Coupang controls critical parts of the value chain, including inventory ownership, fulfillment, last-mile delivery, and customer-facing technology. This structure allows the company to monetize multiple layers of each transaction while maintaining tight control over service quality.
Revenue Engine
The majority of Coupang’s revenue comes from Product Commerce, which includes first-party retail sales of owned inventory and third-party marketplace activity in Korea. Revenue is generated through direct product sales, commissions, logistics and fulfillment fees charged to merchants, advertising tied to product listings and search, and subscription revenue from Rocket WOW memberships. Ownership of inventory and logistics enables Coupang to manage pricing, availability, and delivery speed, turning fulfillment reliability into a competitive advantage.
Ecosystem Expansion
In addition to its core business, Coupang operates Developing Offerings, a collection of newer services designed to increase customer lifetime value and ecosystem depth. These include Coupang Eats, Coupang Play, fintech initiatives, retail operations in Taiwan, advertising products associated with these services, and Farfetch, its global luxury fashion marketplace. Revenue in this segment is primarily driven by Farfetch, food delivery in Korea, and Taiwanese retail operations. While margins vary, these offerings leverage existing infrastructure and customer relationships, allowing scalable growth.
Platform and Economics
Supporting both segments is Coupang’s proprietary e-commerce and logistics platform, which functions as the system layer of the business. Although not a standalone reportable segment, it includes company-owned fulfillment centers, an in-house last-mile delivery network, software-defined routing and inventory management, and data-driven automation. As volume grows, fixed infrastructure costs are spread across more transactions, improving unit economics.
Flywheel Effect
Coupang’s model compounds over time. Faster and more reliable delivery improves customer satisfaction and retention. Higher-order frequency increases infrastructure utilization and data density, lowering per-unit costs. These efficiencies are reinvested into price, speed, and service quality, reinforcing customer loyalty.
Rather than optimizing for short-term margins, Coupang treats logistics and technology as long-term assets. In doing so, it monetizes not just products but also time saved, trust earned, and infrastructure efficiently reused across an expanding commerce ecosystem.
Ecosystem Expansion and Adjacent Businesses
Rocket WOW Memberships
Rocket WOW is the connective tissue of Coupang’s ecosystem. The subscription bundles free and faster delivery with exclusive deals and access to digital services. Its strategic value lies less in direct subscription revenue and more in behavior change. Members tend to order more frequently, rely more heavily on Coupang for everyday needs, and make better use of the logistics network.
For Coupang, WOW improves unit economics by smoothing demand, increasing fulfillment density, and lowering per-order delivery costs. It also creates switching costs by embedding Coupang into daily routines. As with similar programs elsewhere, the membership is best understood as a demand-shaping tool rather than a standalone profit center.
Coupang Eats
Coupang Eats extends the platform into high-frequency, on-demand consumption. Food delivery is structurally competitive and margin-constrained, but it plays an important strategic role. Eats increases daily app engagement, captures incremental customer touchpoints, and improves last-mile utilization during non-peak retail hours.
While profitability in food delivery remains challenging, Coupang’s advantage lies in logistics reuse and customer overlap rather than category leadership. The service strengthens ecosystem stickiness even if near-term margins are thin, making it strategically additive rather than purely financial.
Coupang Play
Coupang Play functions primarily as a retention and engagement lever within the WOW membership rather than a standalone streaming competitor. Content offerings are curated to support loyalty and time spent within the Coupang ecosystem, not to maximize subscription revenue independently.

By bundling entertainment with commerce, Coupang increases perceived value of membership without materially changing customer acquisition costs. The key strength of Coupang Play is discipline. Content spend is measured relative to its impact on retention and order frequency, reducing the risk of runaway costs that have burdened pure-play streaming platforms.
Coupang Play maintains a broad and growing catalog of shows that supports its role as a retention and engagement tool within the Coupang ecosystem.
https://www.coupangplay.com/catalog
Farfetch
The inclusion of Farfetch expands Coupang’s reach into global luxury fashion and introduces a different customer profile and margin structure. Strategically, Farfetch adds international exposure, brand relationships, and a marketplace model that is less logistics-intensive than mass retail.
At the same time, luxury is cyclical and operationally distinct from Coupang’s core strengths. Integration risk, demand volatility, and execution complexity are real considerations. Farfetch’s role within the ecosystem is best viewed as long-term optionality rather than a near-term earnings driver.
Key Implications
These adjacent businesses reinforce Coupang’s shift from a pure retail platform toward a multi-layered commerce ecosystem. Rocket WOW drives frequency and retention, Eats expands daily engagement, Play enhances stickiness, and Farfetch adds international and category diversification. The common thread is infrastructure reuse. Each offering leverages the same logistics, data, and customer relationships, allowing incremental revenue growth with improving capital efficiency over time.
Financial Performance
Revenue Analysis: Scale, Mix, and Momentum
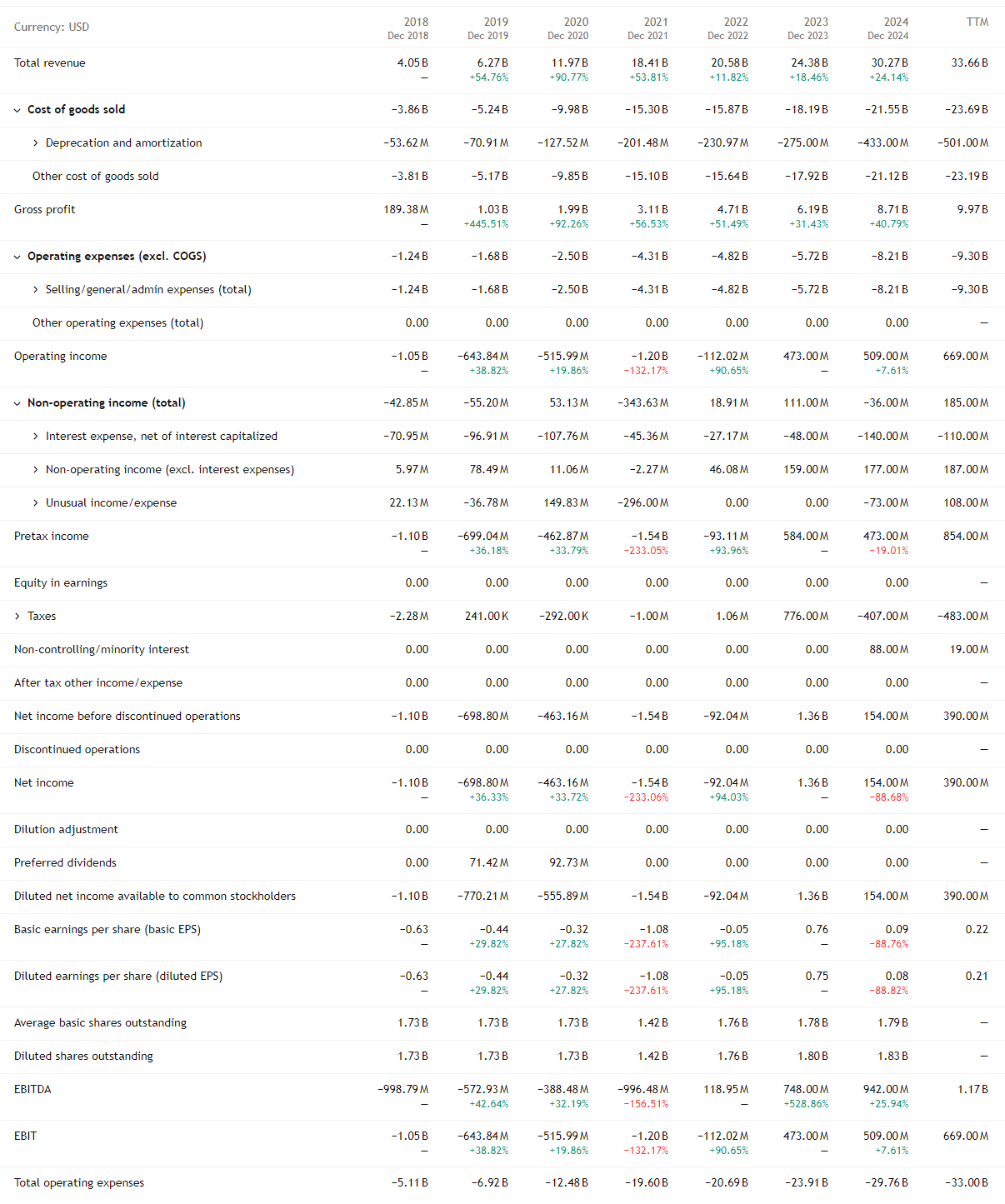
Coupang, Inc. has delivered strong and consistent top-line expansion since 2019, the first year for which standardized and publicly comparable revenue data is available following its transition toward U.S. public company reporting. From 2019 to 2024, total net revenues increased from $6.3 billion to $30.3 billion, nearly a fivefold increase. This trajectory reflects Coupang’s evolution from an aggressive scale-building phase into a more mature, monetization-driven operating model.
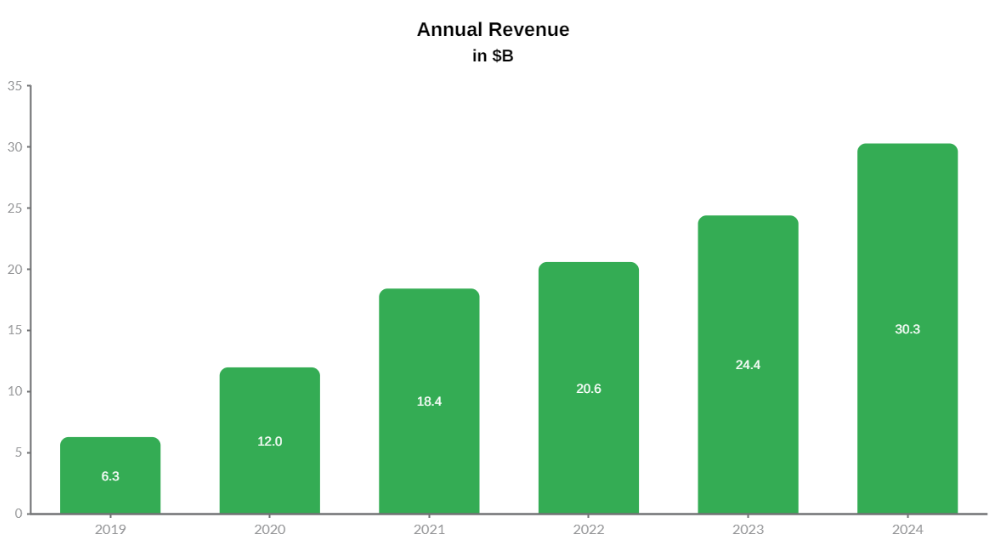
Growth between 2019 and 2021 was marked by hypergrowth, as years of upfront logistics investment began to pay off and e-commerce adoption accelerated sharply. The COVID-19 pandemic acted as an accelerant rather than a disruption. Coupang’s existing fulfillment infrastructure, emphasis on essential goods, and delivery reliability allowed it to absorb surging demand at a time when many retailers faced operational bottlenecks. Importantly, this period was not characterized by a one-time spike, but by lasting customer adoption that carried forward beyond the pandemic.
From 2022 onward, revenue growth moderated in percentage terms but remained strong in absolute dollars, signaling that Coupang had reached meaningful scale in its core market. The increase from $24.4 billion in 2023 to $30.3 billion in 2024 points to renewed momentum driven less by customer acquisition and more by deeper monetization of an established user base. This shift suggests a transition from expansion-led growth to platform-led growth.
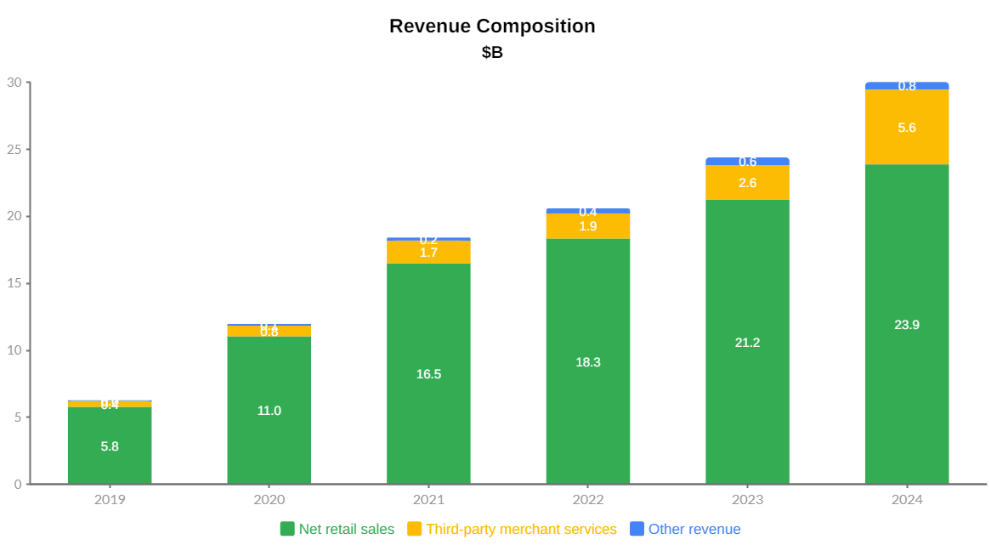
Revenue composition highlights a clear improvement in quality. Net retail sales remain the largest contributor, growing steadily but at a slowing rate as the Korean e-commerce market matures and the structural limits of inventory-heavy retail become more visible. In contrast, third-party merchant services have emerged as the most important structural growth driver, expanding rapidly as marketplace penetration, fulfillment services, and advertising monetization scale. Other revenue streams remain smaller in absolute terms but show consistent growth, reinforcing customer engagement and lifetime value rather than materially impacting near-term totals.
Overall, Coupang’s revenue strengths lie in its scale, improving revenue mix, and increasing operating leverage. Its primary weakness remains continued reliance on capital-intensive retail sales. However, this exposure is partially mitigated by ownership of logistics infrastructure, which enables cross-monetization, higher service reliability, and cost control advantages that asset-light competitors struggle to replicate.
Segment Analysis: Product Commerce and Developing Offerings
Segment-level disclosures have been publicly available since 2020, when Coupang aligned its internal reporting with U.S. disclosure standards. Total segment revenues were driven predominantly by Product Commerce, with Developing Offerings emerging as a meaningful secondary growth contributor.
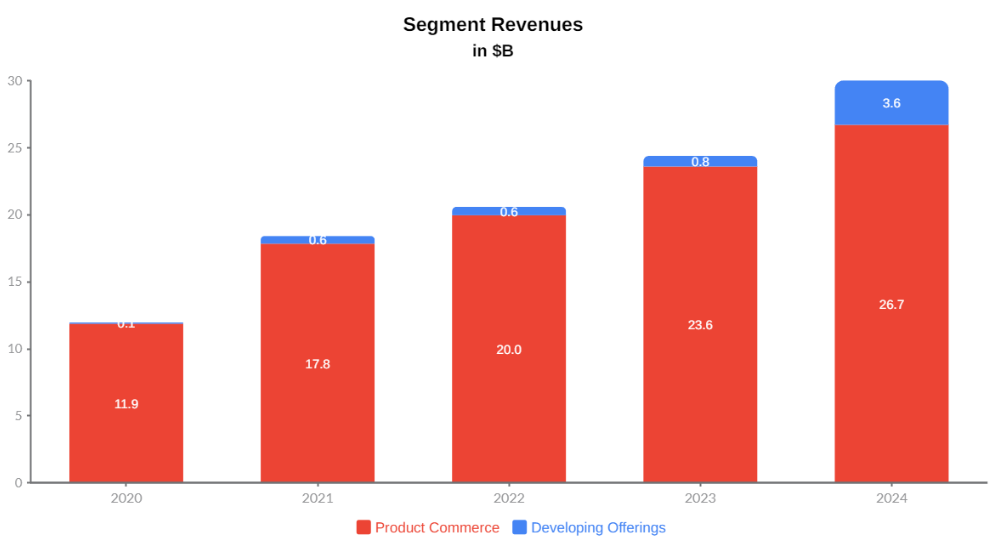
Product Commerce remains the economic backbone of the company. Revenue grew from $11.9 billion in 2020 to $26.7 billion in 2024, supported by high order frequency, consumer trust, and vertically integrated logistics. Growth was strongest in the early years as infrastructure investments paid off and e-commerce adoption surged. More recently, growth has moderated, reflecting market maturity rather than demand weakness. The segment’s key strength is predictability and scale; its main limitation is structural, as inventory ownership and fulfillment intensity constrain margin expansion.
Developing Offerings represent Coupang’s long-term optionality layer. Revenue expanded from $0.1 billion in 2020 to $3.6 billion in 2024, with a pronounced acceleration in the most recent period. Early growth was modest as businesses such as food delivery, streaming, fintech, and international retail were incubated. The sharp increase in 2024 reflects scaling effects, improved monetization, and the inclusion of Farfetch, which significantly expanded the segment’s revenue base. While the segment benefits from lower incremental capital requirements and strong leverage to the existing platform, its heterogeneity introduces variability and limits near-term visibility.
The data shows a company transitioning deliberately from retail-led scale to platform-led monetization. Product Commerce provides stability, volume, and infrastructure utilization, while Developing Offerings drive incremental growth, margin potential, and ecosystem depth. The long-term investment case hinges not on accelerating core retail growth, but on Coupang’s ability to continue shifting its revenue mix toward higher-margin, service-oriented businesses while preserving the operational excellence that underpins its core commerce engine.
Profitability and Margins: Why Net Income and EBITDA Matter
Coupang, Inc.’s net income and EBITDA margins are essential to understanding not just whether the company is profitable, but how its business model matures over time. Margins reveal the sustainability, scalability, and discipline behind that growth.
In general, EBITDA helps isolate operating performance by removing the effects of capital structure, taxes, and non-cash charges, making it particularly useful for companies investing heavily in infrastructure. Net income, by contrast, reflects the full economic outcome after depreciation, stock-based compensation, interest, and taxes. Together, they show whether operating strength is translating into real shareholder value.
General Trend: From Investment Phase to Operating Leverage
Coupang’s profitability profile follows a classic infrastructure-first trajectory. From 2019 through 2021, both net income margin and EBITDA margin were deeply negative, reflecting a period of heavy reinvestment. Net income margins deteriorated sharply through 2020, while EBITDA margins remained negative through 2021, as the company prioritized logistics buildout, workforce expansion, and technology investment over near-term profitability.
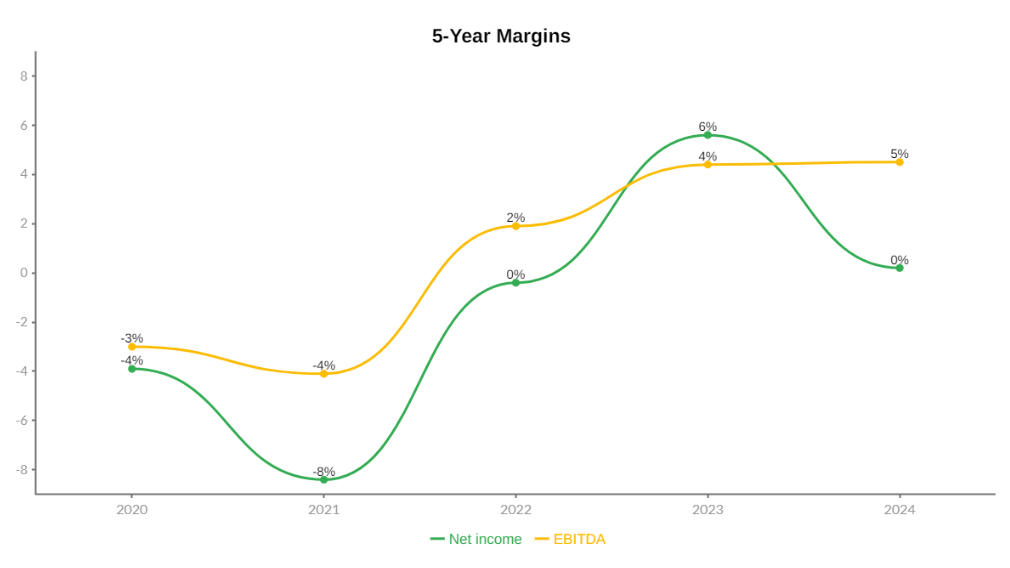
The inflection point emerges between 2021 and 2022, when EBITDA margin turned positive, followed by net income margin moving toward breakeven. This shift is significant, as it indicates that Coupang’s core operations reached sufficient scale for fixed costs to be absorbed across a larger revenue base. The improvement validates the long-term economic logic of Coupang’s vertically integrated model, where upfront infrastructure investment is designed to unlock operating leverage over time.
EBITDA: Indicator of Core Business Health
EBITDA margin improved steadily from deeply negative levels in the early years to consistently positive territory from 2022 onward, reaching a mid-single-digit range by 2024. This sustained improvement suggests that Coupang’s underlying operations are structurally sound and increasingly efficient.
Margin expansion reflects higher fulfillment utilization, improved routing and automation, and a growing contribution from service-based revenues such as third-party merchant fees and advertising. For Coupang, EBITDA margin is particularly informative because depreciation and amortization are elevated due to logistics assets. Positive and expanding EBITDA margins indicate that, even after heavy reinvestment, the operating engine is generating meaningful cash-like earnings.
Net Income: Volatility and Its Implications
Net income margins present a more uneven trajectory. After narrowing materially following 2020, margins turned positive in 2023 before softening again in 2024 toward breakeven levels. This volatility reflects non-operating and accounting factors rather than a deterioration in core operations, including elevated depreciation from logistics infrastructure, stock-based compensation, integration costs related to Developing Offerings, and macro-driven expense variability.
Such fluctuations are common for companies transitioning from infrastructure buildout to optimization. Importantly, the ability to maintain near-breakeven net income margins despite sustained reinvestment and positive EBITDA margins suggests that Coupang continues to prioritize long-term value creation over short-term earnings maximization.
Why the Negatives Matter, and Why They Are Not Fatal
Negative margins in earlier years are often misinterpreted as business weakness. In Coupang’s case, they represent intentional value creation ahead of monetization. The losses funded infrastructure that competitors cannot easily replicate. The key risk would be persistent EBITDA losses, which would indicate structural inefficiency. Instead, Coupang’s EBITDA trajectory shows improving operating leverage, mitigating concerns about long-term viability.
The remaining weakness lies in net income consistency. Until depreciation, stock-based compensation, and ecosystem investments stabilize relative to revenue, net margins may remain volatile. This affects valuation optics but does not undermine the operating thesis.
For Coupang, EBITDA margins confirm that the business model works at scale, while net income highlights the trade-off between reinvestment and reported profitability. More broadly, these metrics are essential in evaluating platform companies because they distinguish between temporary losses driven by strategy and structural losses driven by flawed economics. Coupang’s margin evolution suggests it has crossed the hardest part of the curve: proving that growth can translate into operating profitability, even if reported earnings remain uneven in the near term.
Market Overview: Retail and Internet Commerce in 2026
According to industry research from the Deloitte Consumer Industry Center and the National Retail Federation, the global retail and internet commerce sector is entering a pivotal phase in 2026. While the foundational principles of retail — customer centricity, operational discipline, and financial prudence — remain unchanged, the industry is undergoing structural shifts that demand greater adaptability, technological maturity, and cost discipline.
Despite expectations of modest global economic slowing, sentiment among retail executives remains broadly constructive. Most industry leaders anticipate revenue growth and margin expansion, underpinned by productivity initiatives, technology-enabled efficiencies, and tighter capital allocation. However, this optimism is conditional. Retailers that fail to adapt to evolving consumer behavior, AI-led commerce models, and persistent cost pressures risk falling behind.
Structural Shift Toward Value-Seeking Consumers
Both Deloitte and NRF point to a lasting shift toward value-seeking behavior across income levels. Consumers are rethinking what “fair value” means, with price sensitivity now extending beyond lower-income households to more affluent consumers. This change reflects a structural reset in expectations rather than a temporary response to inflation.
At the same time, value is no longer defined by price alone. Factors such as reliability, convenience, ease of checkout, loyalty programs, service quality, and trust play a meaningful role in how consumers evaluate value. Retailers that combine affordability with a strong, reliable experience are better positioned to maintain demand and protect pricing power in a more cost-conscious environment.
AI-Led Commerce: From Enablement to Infrastructure
Artificial intelligence is transitioning from experimentation to execution across the retail sector. By 2026, AI is increasingly embedded into core operations, spanning demand forecasting, inventory optimization, pricing, personalization, marketing automation, and supply chain management. Both Deloitte and NRF emphasize the rise of agentic AI, where autonomous systems increasingly mediate product discovery, decision-making, and transactions.
This shift has material implications for internet retail. As shopping journeys compress into AI-driven interfaces, traditional discovery channels such as search engines, social media, and brand-led funnels may weaken. Retailers must ensure that product data, pricing, and availability are structured, accurate, and optimized for AI readability to remain visible within these emerging ecosystems. Competitive advantage increasingly depends on clean data architecture, system interoperability, and organizational readiness to operate alongside AI tools.
Marketing, Customer Experience, and Data Monetization
Marketing and customer engagement are being reshaped by AI-enabled personalization and analytics. Retailers are increasingly internalizing marketing capabilities, supported by automation, dynamic content generation, and real-time decision support. This trend is particularly relevant for retailers operating retail media networks, which are emerging as higher-margin revenue streams through the monetization of first-party customer data.
At the same time, the industry faces heightened complexity in customer engagement. Younger cohorts expect seamless omnichannel journeys, authenticity, and personalization, while exhibiting lower brand loyalty and greater sensitivity to missteps. As a result, differentiation is shifting away from channel presence alone toward the quality of experience, relevance, and trust embedded in customer interactions.
Supply Chain Resilience as a Strategic Imperative
Supply chain transformation remains a central focus entering 2026. Rising trade costs, geopolitical uncertainty, and policy-driven disruptions are prompting retailers to diversify sourcing, pursue nearshoring strategies, and invest in technology-enabled visibility and flexibility. AI-driven forecasting and inventory management are increasingly viewed as essential tools for balancing service levels with working capital efficiency.
Rather than treating supply chain resilience as a defensive measure, leading retailers are reframing it as a competitive advantage. Faster response to demand signals, improved fulfillment reliability, and reduced inventory volatility are becoming differentiators in a value-conscious and service-sensitive market.
Margin Management and Financial Discipline
Margin pressure persists across the industry due to rising labor, logistics, and input costs. Both Deloitte and NRF emphasize that financial fortitude in 2026 will depend less on aggressive growth and more on precision. Retailers are adjusting pricing structures, refining product mix, raising free-shipping thresholds, and reallocating capital toward higher-return initiatives.
Cost discipline is increasingly embedded across sourcing, fulfillment, and pricing decisions, supported by data-led promotions and automation. Retailers that successfully balance margin protection with customer trust are better positioned to sustain profitability in an environment where consumers remain price-aware but service-expectant.
Industry Implications
The 2026 retail environment favors companies with scale, integrated systems, and strong execution. Shifts in consumer behavior, AI-driven commerce, supply chain uncertainty, and margin pressure are interconnected challenges, not separate issues. Retailers that treat adaptability as a core capability — supported by infrastructure, data, and customer insight — are more likely to remain resilient.
For internet retail and logistics-led platforms, success increasingly depends on ecosystem depth, operational control, and technology maturity. Competitive advantage is less about individual features and more about coordinating commerce, fulfillment, and customer engagement within a single, integrated system.
Competition and Peer Comparison
Revenue Performance Across Peers
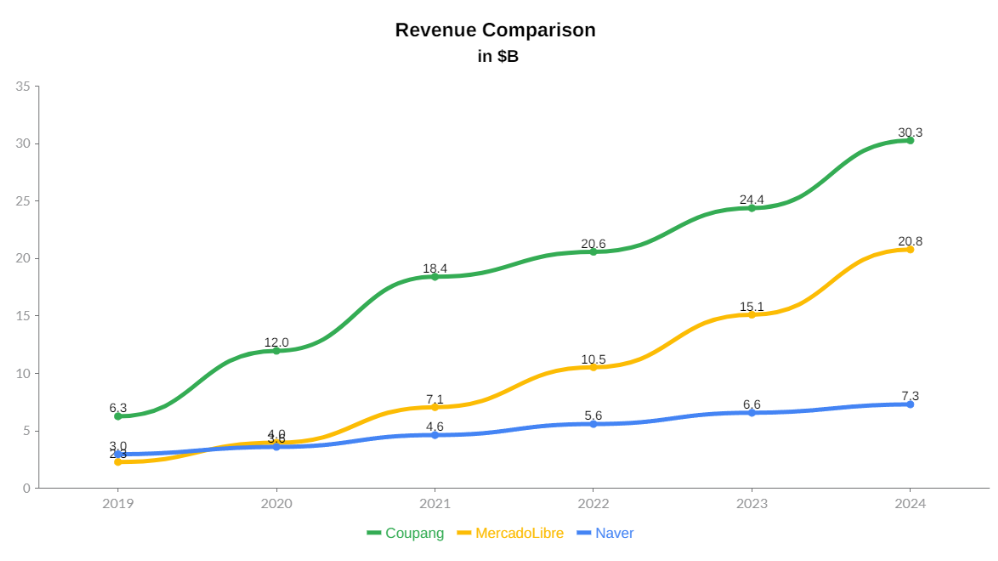
The chart above compares revenue growth for Coupang, MercadoLibre, and Naver from 2019 to 2024. These peers were selected deliberately, not because they are identical businesses, but because each represents a distinct competitive and strategic benchmark relevant to Coupang’s positioning.
Why MercadoLibre and Naver Are the Right Comparables
MercadoLibre (MeLi) serves as a global structural analogue. Like Coupang, it operates a scaled e-commerce platform in a developing-to-developed digital commerce market, has invested heavily in logistics and fulfillment, and has expanded into adjacent services such as payments and advertising. MeLi represents what a successful, regionally dominant e-commerce platform can look like when operating leverage begins to materialize. Comparing Coupang to MeLi helps frame whether Coupang’s growth and scale are competitive with leading global platform peers, even across different geographies.
Naver, by contrast, is Coupang’s most relevant domestic competitive benchmark. While Naver is not a pure e-commerce company, it dominates discovery, search, and online traffic in South Korea and plays a critical role in commerce through Naver Shopping and marketplace integrations. Including Naver highlights the contrast between an asset-light, traffic-driven commerce model and Coupang’s asset-heavy, logistics-driven model, which is central to understanding Coupang’s strategic differentiation.
Together, MeLi and Naver bracket Coupang’s competitive landscape: MeLi as a global e-commerce platform peer and Naver as the most powerful local ecosystem competitor.
Revenue Trajectories and What They Show
From 2019 to 2024, Coupang’s revenue growth clearly outpaces both comparables in absolute scale. Coupang’s revenues expanded from roughly $6.3 billion to over $30 billion, reflecting rapid penetration, high order frequency, and the effectiveness of its vertically integrated logistics model. By 2024, Coupang generates meaningfully more revenue than both MeLi and Naver, despite operating primarily in a single core geography.
MercadoLibre shows strong and accelerating growth over the same period, rising from approximately $2.3 billion to over $20 billion. This reinforces MeLi’s status as a successful regional platform, but also highlights that Coupang reached larger absolute scale faster, despite South Korea being a smaller population market than Latin America. This suggests higher per-customer monetization and deeper engagement rather than reliance on geographic breadth.
Naver’s commerce-related revenues grow more steadily, from roughly $3.0 billion to about $7.3 billion, reflecting a mature, diversified internet business where commerce is one of several monetization channels rather than the core engine. Naver’s slower growth relative to Coupang underscores the limits of an asset-light commerce strategy when delivery speed, reliability, and fulfillment control become primary drivers of consumer preference.
Competitive Strengths Highlighted by the Comparison
The comparison highlights several core strengths in Coupang’s competitive position:
- Scale leadership in core commerce: Coupang’s revenue base is significantly larger than its closest local and global comparables, giving it scale advantages in logistics utilization and cost absorption.
- Faster monetization per market: Achieving MeLi-level scale in a single-country market suggests strong customer penetration and high order frequency.
- Structural differentiation vs. Naver: Coupang competes less on discovery and more on execution, reliability, and speed, areas where asset-light competitors struggle to match performance without similar infrastructure investment.
At the same time, the comparison implicitly highlights trade-offs. Coupang’s scale advantage comes with higher capital intensity and operating risk relative to Naver, while MeLi’s geographic diversification reduces single-market exposure. These differences reinforce that Coupang’s moat is operational rather than distribution-driven.
Using MercadoLibre and Naver as comparables provides a balanced view of Coupang’s competitive standing. The revenue data supports the view that Coupang has built a category-defining commerce platform in South Korea, with scale and growth that compare favorably to leading global e-commerce peers and materially exceed domestic ecosystem competitors. The key competitive question going forward is not whether Coupang can grow revenue faster than peers, but whether it can continue converting that scale advantage into durable margins and long-term economic returns.
EBITDA Margin Comparison and Peer Context
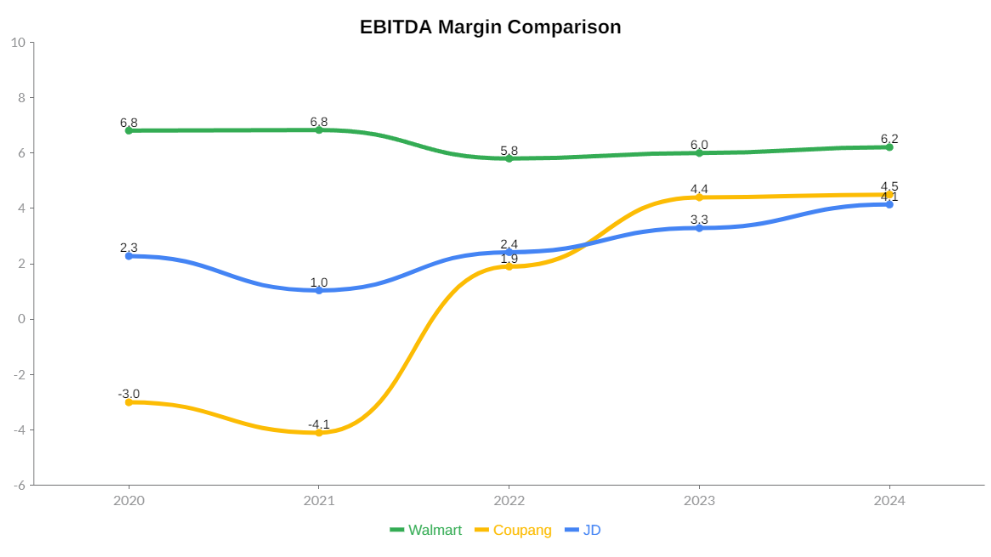
The chart above compares EBITDA margins for Coupang, Walmart, and JD.com from 2020 to 2024. While Walmart and JD were not used as primary revenue comparables due to their significantly larger scale, they are appropriate benchmarks for EBITDA margin comparison because they operate logistics-intensive retail and e-commerce models with comparable cost structures.
Why EBITDA Margin Is the Right Metric Here
EBITDA margin is particularly useful when comparing companies with different capital intensity, accounting treatments, and stages of maturity. EBITDA removes the effects of depreciation, amortization, taxes, and financing decisions, allowing for a clearer view of core operating efficiency. This is especially relevant for companies that own and operate large logistics networks, where depreciation can materially distort bottom-line profitability.
For Coupang, EBITDA margin provides the most transparent signal of whether its infrastructure-heavy strategy is generating operating leverage. Comparing this metric against Walmart and JD helps frame Coupang’s performance relative to peers that have already achieved scale and operational maturity in logistics-driven commerce.
Interpreting the Margin Trends
Walmart consistently reports the highest EBITDA margins across the period, reflecting its massive scale, purchasing power, and highly optimized supply chain. These margins are the result of decades of operational refinement and a diversified business mix, making Walmart a benchmark for logistics efficiency rather than a direct competitive peer for Coupang.
JD.com exhibits moderate but steadily improving EBITDA margins, consistent with its logistics-intensive e-commerce model. Operating in a different market and at a more advanced stage of scale, JD’s margin profile illustrates how infrastructure-heavy platforms can gradually improve profitability as utilization increases and fixed costs are absorbed.
Coupang’s EBITDA margin trajectory shows the clearest evidence of operating leverage emerging. After operating at negative margins through 2021, Coupang turned EBITDA-positive in 2022 and continued to expand margins through 2024. By 2024, Coupang’s EBITDA margin had surpassed JD’s, highlighting meaningful gains in fulfillment efficiency, cost absorption, and revenue mix quality.
While Coupang’s margins remain below Walmart’s, this gap is expected given Coupang’s earlier position in its maturity curve, continued reinvestment in ecosystem expansion, and focus on a single, highly competitive market. Importantly, Coupang’s rise to a leading position among its more structurally comparable peers reflects progress rather than underperformance. At this stage, the direction and consistency of margin improvement are more informative than absolute margin levels, reinforcing the long-term potential of Coupang’s vertically integrated model.
What the Comparison Tells Us
This EBITDA margin comparison reinforces two key points. First, Coupang’s business model is working. The shift from negative to positive EBITDA and continued margin expansion indicate that its logistics and platform investments are translating into operational efficiency. Second, there remains meaningful upside. As utilization improves and growth moderates, Coupang has room to narrow the margin gap with more mature peers.
Overall, including EBITDA margin alongside revenue comparisons provides a more balanced view of Coupang’s competitive position. While Coupang may not yet be the strongest on margins, its trajectory aligns with what has historically preceded durable profitability in logistics-led commerce platforms.
Leadership, Governance, and Compensation
Founder and Executive Leadership

Bom Kim
Founder, Chief Executive Officer, and Chairman of the Board
Bom Kim’s path to founding Coupang is closely tied to a single, persistent insight: commerce should exist to save people time, not create friction.
Born in South Korea and educated in the United States, Kim attended Harvard University before leaving to pursue entrepreneurship. Early in his career, he founded several ventures focused on content and education, experiences that shaped his conviction that technology should simplify everyday life. When he returned his attention to commerce in 2010, South Korea presented a paradox. It was one of the world’s most densely populated and digitally connected countries, yet online shopping remained slow, inconvenient, and unreliable. Kim identified logistics, not demand, as the core constraint.
Rather than building a discount-driven marketplace, Kim made the defining decision that still shapes Coupang today: to own the customer experience end to end. This meant building proprietary fulfillment centers, developing in-house software for inventory and routing, and operating a last-mile delivery network instead of relying on third parties. At the time, this approach was widely viewed as impractical and capital-intensive for a startup. Kim pursued it anyway, believing that logistics was not a cost center but the product itself.
Under his leadership, Coupang prioritized long-term infrastructure over short-term profitability. From Rocket Delivery to dawn delivery and frictionless returns, many of Coupang’s signature features were not incremental improvements but structural changes that reset consumer expectations. Kim consistently chose scale, reliability, and trust even when it meant sustained losses and external skepticism.
Kim’s leadership style is marked by customer obsession and operational rigor. He is known for focusing the organization around a small number of non-negotiable principles, particularly speed, reliability, and simplicity. Internally, Coupang operates less like a traditional retailer and more like a systems engineering organization, with software and logistics tightly integrated. This discipline has allowed the company to translate scale into operating leverage as infrastructure utilization improves.
A notable aspect of Kim’s leadership is his willingness to delay recognition. Coupang’s IPO did not mark a strategic shift toward short-term earnings optimization. Instead, Kim continued reinvesting in logistics, automation, and ecosystem expansion, signaling a long-term orientation aligned with infrastructure-style businesses rather than consumer apps chasing quick margins.
Today, Kim’s influence is visible not just in Coupang’s size, but in how it operates. The company’s vertically integrated model, its tolerance for early losses in pursuit of durable advantage, and its framing of commerce as a time-saving utility all trace back to the founder’s original thesis. Coupang’s wins to date are less the result of tactical execution and more the outcome of a decade-long commitment to a singular strategic belief, consistently applied.
Other Key Leaders and Governance
While Bom Kim defines Coupang’s long-term vision and operating philosophy, execution at scale depends on experienced leaders across finance, governance, and administration.
Gaurav Anand
Chief Financial Officer
Gaurav Anand plays a central role in translating Coupang’s infrastructure-led strategy into a financially sustainable model. As CFO, he oversees capital allocation, financial planning, and investor communications during a critical transition period from aggressive reinvestment toward operating leverage.
Anand’s tenure has coincided with:
- Coupang’s progression to sustained positive EBITDA
- Improved financial transparency and segment reporting following its U.S. IPO
- Balance sheet management during periods of net income volatility
His contribution is particularly important given Coupang’s capital-intensive logistics footprint. Anand’s role has been to ensure that long-term infrastructure investments remain disciplined, well-funded, and aligned with a credible path toward durable profitability rather than short-term earnings optimization.
Harold Rogers
General Counsel and Chief Administrative Officer
Harold Rogers oversees Coupang’s legal, compliance, governance, and administrative functions, playing a key role in supporting the company’s evolution as a large, U.S.-listed technology and logistics platform. In this capacity, he is responsible for ensuring regulatory compliance, corporate governance standards, and institutional processes across Coupang’s complex and highly regulated operating environment.
Rogers’ responsibilities include:
- Oversight of legal and regulatory matters across jurisdictions
- Governance and compliance frameworks appropriate for a public company
- Administrative and organizational infrastructure supporting scaled operations
His role is particularly important given Coupang’s labor-intensive logistics network, data-driven platform, and exposure to evolving regulatory expectations. By strengthening governance, compliance, and internal controls, Rogers contributes to institutional stability as Coupang transitions from a rapid buildout phase toward operational maturity and sustained execution.
Board Oversight and Institutional Depth
Coupang’s leadership is complemented by an active Board of Directors composed of experienced operators, investors, and governance professionals. In addition to Bom Kim, the board includes figures such as Neil Mehta, Jason Child, and Pedro Franceschi, among others, who bring backgrounds spanning technology, global finance, private equity, and public company governance.
The presence of a diversified board helps balance founder-led vision with institutional oversight, particularly as Coupang navigates regulatory complexity, capital allocation decisions, and ecosystem expansion. For investors, this governance structure provides an additional layer of accountability beyond individual executives and reinforces the company’s evolution from founder-led startup to global public enterprise.
Executive Compensation and Alignment with Shareholders
Discussing executive compensation is an important part of an investment thesis and any stock recommendation because it provides insight into governance quality, incentive alignment, and management priorities. How executives are paid often signals whether leadership is incentivized to pursue short-term financial optics or long-term value creation, which is particularly relevant for platform businesses like Coupang that require sustained reinvestment.
Compensation Structure and Philosophy
Coupang determines executive compensation through arm’s-length negotiations, overseen by its Compensation Committee and Section 16 Equity Committee. Pay decisions are informed by market benchmarking, guidance from external compensation consultants, internal role comparisons, and the strategic importance of each position. Importantly, Coupang emphasizes equity-based, long-term compensation, with a significant portion of executive pay tied to stock awards that vest over multiple years.
This structure reflects management’s stated objective of aligning executive incentives with long-term stockholder value rather than short-term earnings targets. In a capital-intensive business model, this approach reduces pressure to prematurely optimize margins at the expense of customer experience or infrastructure investment.
What the 2024 Data Shows
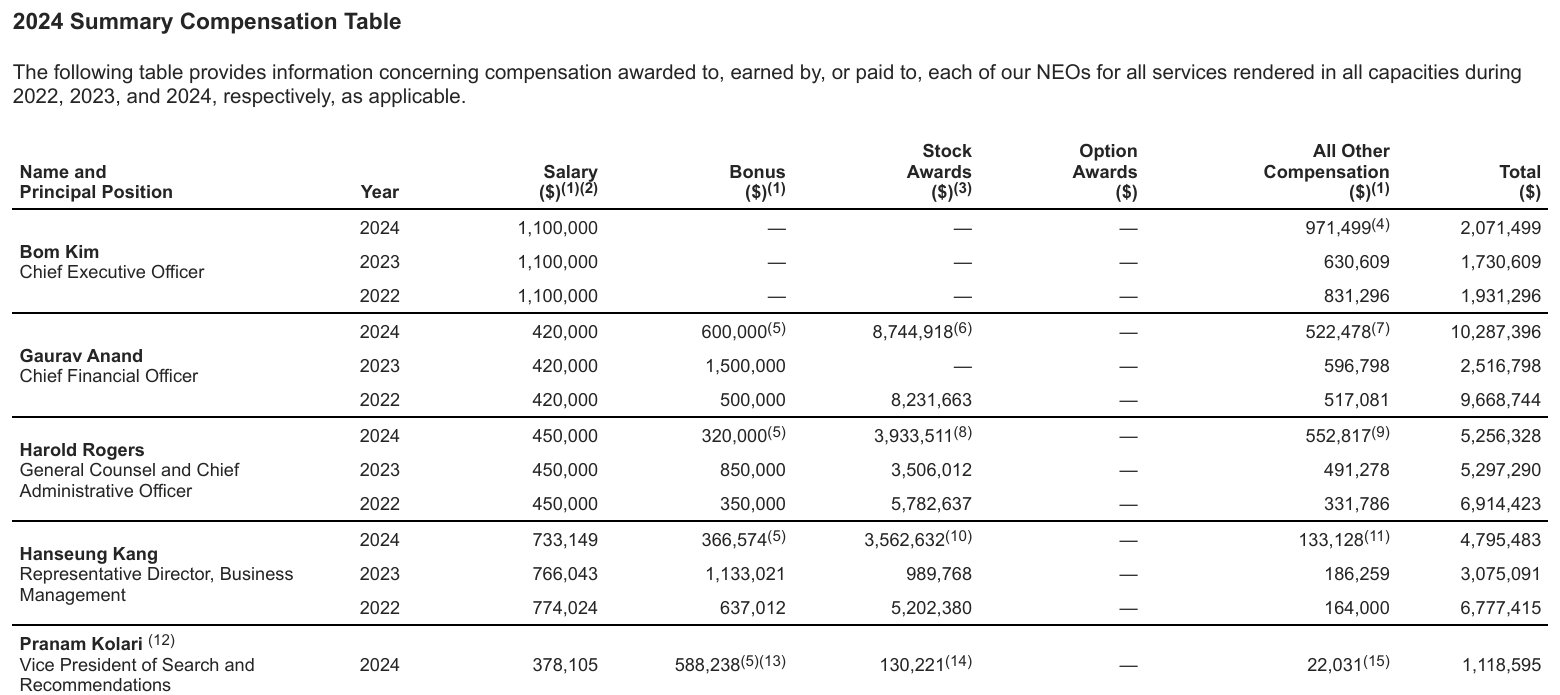
The 2024 Summary Compensation Table highlights clear differentiation by role:
- Bom Kim, as Founder and CEO, receives a relatively modest fixed salary compared to the scale of the company, with limited annual cash incentives. This reinforces his long-term orientation and alignment with equity value rather than near-term compensation extraction.
- Gaurav Anand, as CFO, receives a more traditional mix of base salary, bonus, and stock awards, reflecting the increasing importance of financial discipline, reporting rigor, and operating leverage as Coupang matures.
- Other senior executives show a similar pattern: base compensation is competitive but not excessive, while total pay is meaningfully influenced by stock awards and performance-linked components.
The absence of outsized cash bonuses across the leadership team suggests a deliberate effort to avoid short-term incentive distortions, particularly during periods of ongoing investment and margin transition.
Implications for Investors
For potential investors, Coupang’s executive compensation framework supports several positive conclusions:
- Long-term alignment: Multi-year equity awards tie management wealth creation to sustained stock performance rather than annual results.
- Governance discipline: Oversight by independent committees and external benchmarking reduces the risk of excessive or misaligned pay.
- Strategic consistency: Compensation design reinforces Coupang’s willingness to prioritize infrastructure, customer experience, and ecosystem development over short-term profitability.
At the same time, investors should recognize that equity-heavy compensation increases dilution over time, making execution and value creation critical. The effectiveness of this compensation model ultimately depends on whether management continues to translate scale and operating leverage into durable returns.
Coupang’s executive compensation structure is broadly consistent with a long-term, platform-driven investment case. By emphasizing equity-based incentives and downplaying short-term cash rewards, the company aligns leadership behavior with the interests of long-term shareholders. For an investment thesis, this supports confidence in management’s commitment to disciplined growth rather than short-term financial engineering.
Strategic Initiatives: What Comes Next
At this stage of its evolution, Coupang is no longer defined by whether it can scale, but by how effectively it can convert scale into durable economics. The company’s strategic initiatives reflect this shift, emphasizing discipline, efficiency, and selective expansion rather than rapid footprint growth.
Deepening Logistics Efficiency and Automation
Coupang’s foremost strategic priority remains improving the productivity of its logistics network. With national-scale infrastructure already in place, incremental gains now come from higher utilization, better routing, automation, and technology-driven optimization. These efforts are central to expanding EBITDA margins, as fixed logistics costs are spread across a growing and more frequent order base. Rather than building new capacity aggressively, Coupang is increasingly focused on extracting more value from what it already owns.
Expanding Higher-Margin Platform Services
Coupang continues to emphasize growth in service-based revenues, particularly third-party merchant services, advertising, and Rocket WOW memberships. These offerings improve revenue mix by adding scalable, higher-margin layers on top of core retail transactions. Strategically, this reduces reliance on first-party inventory growth while increasing customer lifetime value and monetization per order. Advertising and merchant tools, in particular, benefit from high-intent traffic within the ecosystem without requiring proportional increases in capital investment.
Strengthening the Ecosystem Without Overextension
Ecosystem expansion remains deliberate rather than expansive. Services such as Coupang Eats and Coupang Play are positioned as engagement and retention tools rather than standalone profit centers. Their role is to increase frequency, app stickiness, and infrastructure utilization. Similarly, Farfetch represents selective international and category exposure, offering long-term optionality without redefining Coupang’s core identity. Management’s approach suggests a preference for adjacent depth over geographic sprawl.
Leveraging Data and AI Across Operations
Aligned with broader industry trends, Coupang is increasingly integrating data and AI into forecasting, inventory management, personalization, and operational decision-making. These initiatives are less visible to consumers but strategically important. Improved demand prediction, smarter promotions, and more efficient fulfillment all support margin expansion while maintaining service quality. Over time, these capabilities reinforce Coupang’s execution advantage over asset-light competitors.
Maintaining Capital and Governance Discipline
Finally, Coupang’s strategic initiatives are underpinned by capital allocation and governance discipline. Executive compensation structures emphasize long-term equity value, reinforcing a focus on sustainable performance rather than short-term financial targets. This alignment supports continued reinvestment where returns are attractive, while avoiding pressure to prematurely optimize margins at the expense of customer experience or operational reliability.
Strategic Perspective
Coupang’s strategy going forward is not about doing more, but about doing better. By prioritizing efficiency, higher-quality revenue, and disciplined ecosystem expansion, the company is positioning itself to move from a scale-driven growth story to one defined by operating leverage and long-term value creation.
Risks and Considerations
All investments carry risk, and Coupang is no exception. While this thesis focuses on structural strengths and long-term potential, a balanced assessment requires acknowledging the key risks that could impair execution, profitability, or valuation. A comprehensive list of risks is detailed in Coupang’s annual reports; the discussion below highlights the most material considerations for investors.
Execution and Operational Risk
Coupang’s business model depends on flawless execution across a complex, asset-heavy logistics network. Disruptions related to labor availability, wage inflation, automation delays, or last-mile delivery efficiency could materially affect service quality and cost structure. Because Coupang owns much of its fulfillment and delivery infrastructure, operational missteps are more directly borne by the company than by asset-light competitors.
Margin and Cost Structure Risk
Despite improving EBITDA, Coupang’s margins remain sensitive to fulfillment costs, labor expenses, and competitive pricing pressure. The company continues to reinvest aggressively, which can suppress net income and create earnings volatility. If operating leverage fails to materialize as expected, particularly in Product Commerce, long-term profitability could fall short of investor expectations.
Competitive Intensity
E-commerce and digital services are highly competitive. Coupang faces competition from domestic and global players across retail, food delivery, streaming, and fintech. Sustained price competition or increased promotional intensity could pressure margins, slow revenue growth, or force higher marketing spend to defend market share.
Regulatory and Labor Risk
Coupang operates in heavily regulated environments, particularly around labor practices, workplace safety, data privacy, and consumer protection. Changes in labor laws, delivery worker classification, or compliance requirements could increase costs or restrict operational flexibility. Regulatory scrutiny may intensify as Coupang’s scale and influence grow.
Ecosystem and Expansion Risk
Developing Offerings, while strategically important, introduce additional uncertainty. Businesses such as food delivery, content streaming, fintech, and international operations carry different risk profiles and may take longer to achieve profitability. Integration risks related to acquisitions, including Farfetch, could distract management or dilute returns if synergies fail to materialize.
Macroeconomic and Consumer Risk
Coupang’s performance is influenced by consumer spending, inflation, interest rates, and broader economic conditions. Economic slowdowns may reduce discretionary spending, increase price sensitivity, or raise operating costs. Currency fluctuations can also impact reported results, particularly as international operations expand.
Valuation and Market Risk
Even a strong business can be a poor investment at the wrong price. Coupang’s valuation depends on investor confidence in its ability to translate scale into durable profitability. Shifts in market sentiment toward growth-oriented or capital-intensive companies could lead to share price volatility independent of underlying performance.
Key Person and Strategic Risk
Coupang’s long-term vision and execution have been closely tied to its leadership. Loss of key executives, misalignment in strategic priorities, or execution drift could weaken the company’s competitive positioning over time.
Overall Risk Assessment
Coupang’s risks are not unique, but they are magnified by the company’s scale, ambition, and capital intensity. The investment case rests on the belief that management can continue converting infrastructure investments into operating leverage while navigating competitive, regulatory, and macroeconomic pressures. Investors should view Coupang not as a risk-free compounder, but as a long-term platform investment where returns are earned through patience, tolerance for volatility, and disciplined risk assessment.
From Scale to Substance
The analysis of Coupang presents a company that has largely completed its scale-building phase and is now transitioning toward monetization and operating leverage. Coupang has built a structurally differentiated commerce platform anchored in owned logistics, high service reliability, and deep customer engagement. This model has allowed it to achieve revenue scale that compares favorably with global platform peers, despite operating primarily within a single core market.
Financially, the trajectory supports this narrative. Revenue growth has remained strong, while EBITDA margins have turned sustainably positive, signaling that the underlying operating engine is working as intended. While net income remains volatile, this reflects deliberate reinvestment choices rather than structural weakness. Compared with mature logistics-led peers, Coupang’s margin profile is still developing, but the direction of travel aligns with what historically precedes durable profitability in infrastructure-heavy platforms.
Coupang’s ecosystem expansion, including Rocket WOW, Eats, Play, and selective international exposure, reinforces customer lifetime value and infrastructure utilization rather than distracting from the core business. These adjacencies provide optionality and upside without fundamentally altering the company’s strategic focus. At the same time, management and compensation structures emphasize long-term equity value, supporting alignment between leadership incentives and shareholder outcomes.
Risks remain. Coupang operates in a highly competitive environment, faces ongoing cost pressures, and remains exposed to execution and regulatory challenges. Its asset-heavy model also demands continued discipline as growth moderates. However, these risks are balanced by meaningful barriers to replication, rooted in logistics density, data, and operational complexity.
Overall, Coupang represents a platform business where the hardest work—building scale, infrastructure, and customer trust—has largely been done. The investment case now hinges less on whether Coupang can grow, and more on how effectively it can convert its scale advantage into sustained margins and long-term shareholder value.
🔗 Explore our long-term investing philosophy at Snowball Investing.
🔗 Understand why Page Industries fits into a durable portfolio in The Essentials of Snowball Investing.
🔗 Browse our curated list of investing books we recommend for long-term investors.
🎧 Listen to audio versions of select articles on the Snowball Investing Podcast.
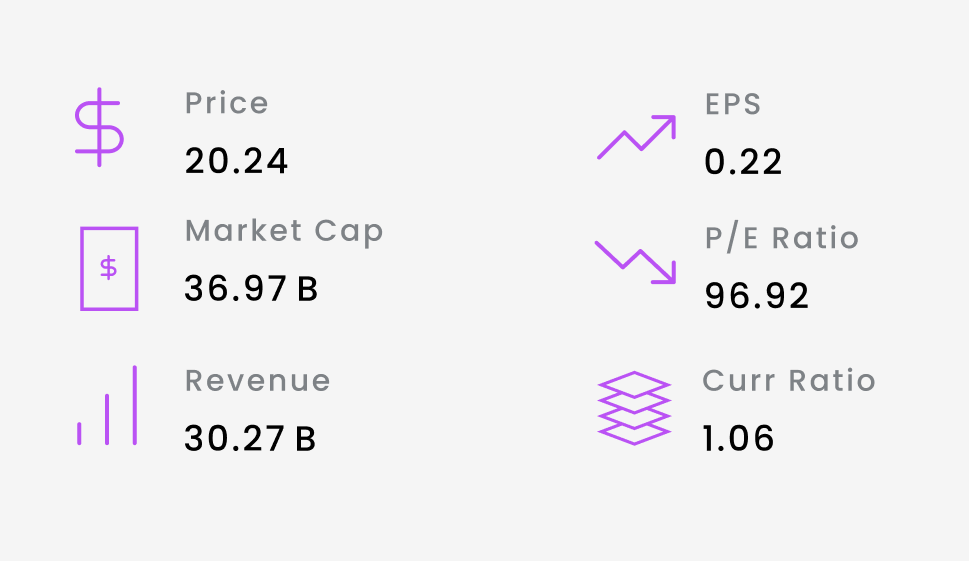
The following data snapshots are as of 1/21/2026 from tradingview website
Key Stats
Performance
Financial Statements
Income Statement
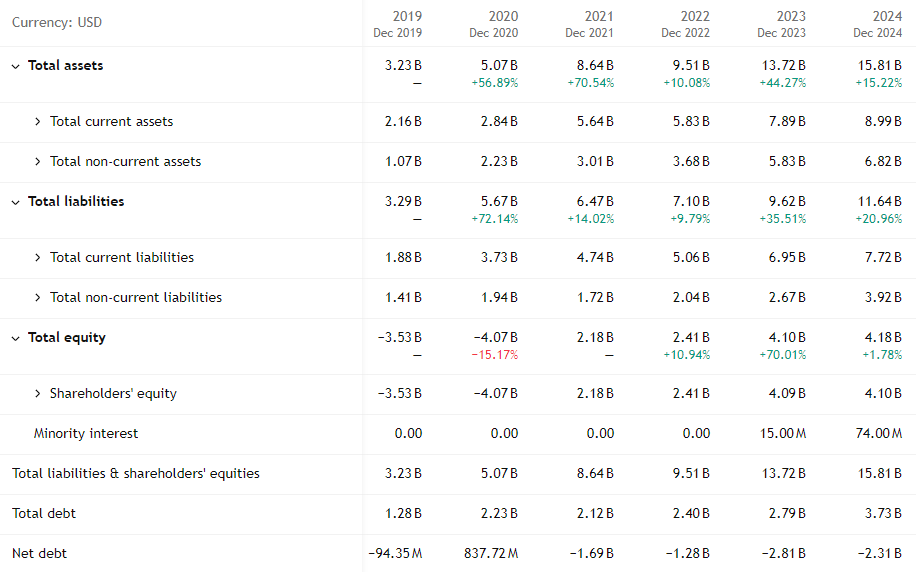
Balance Sheet
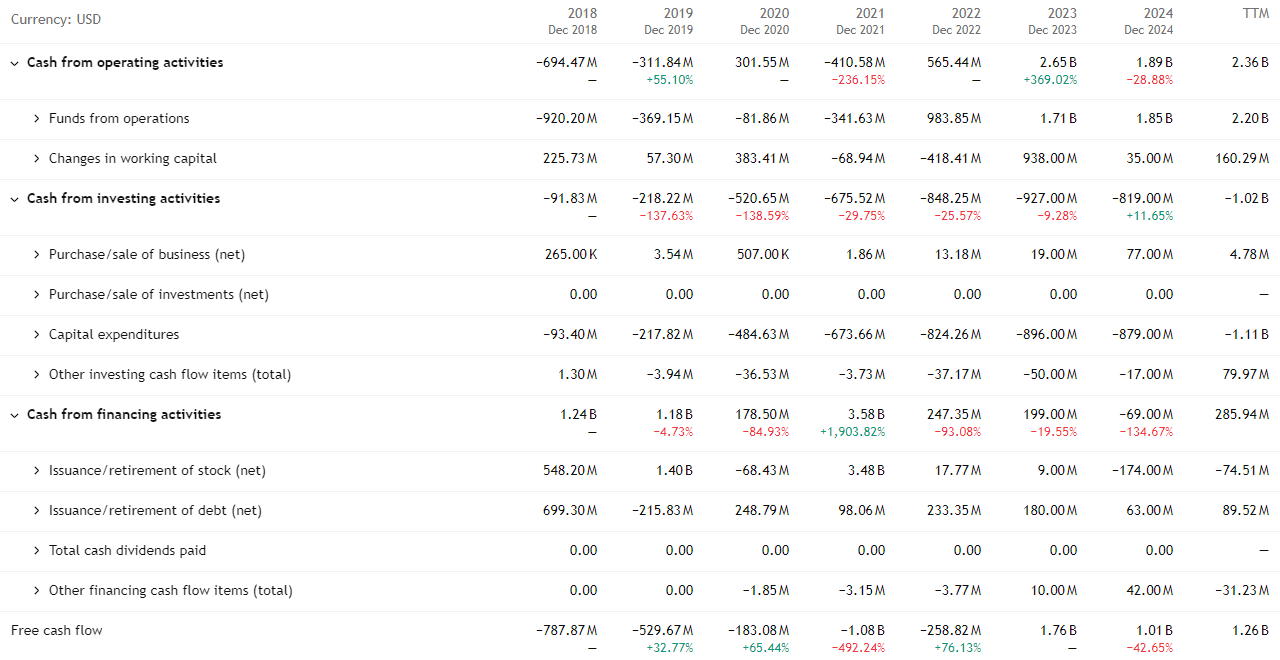
Cash Flow
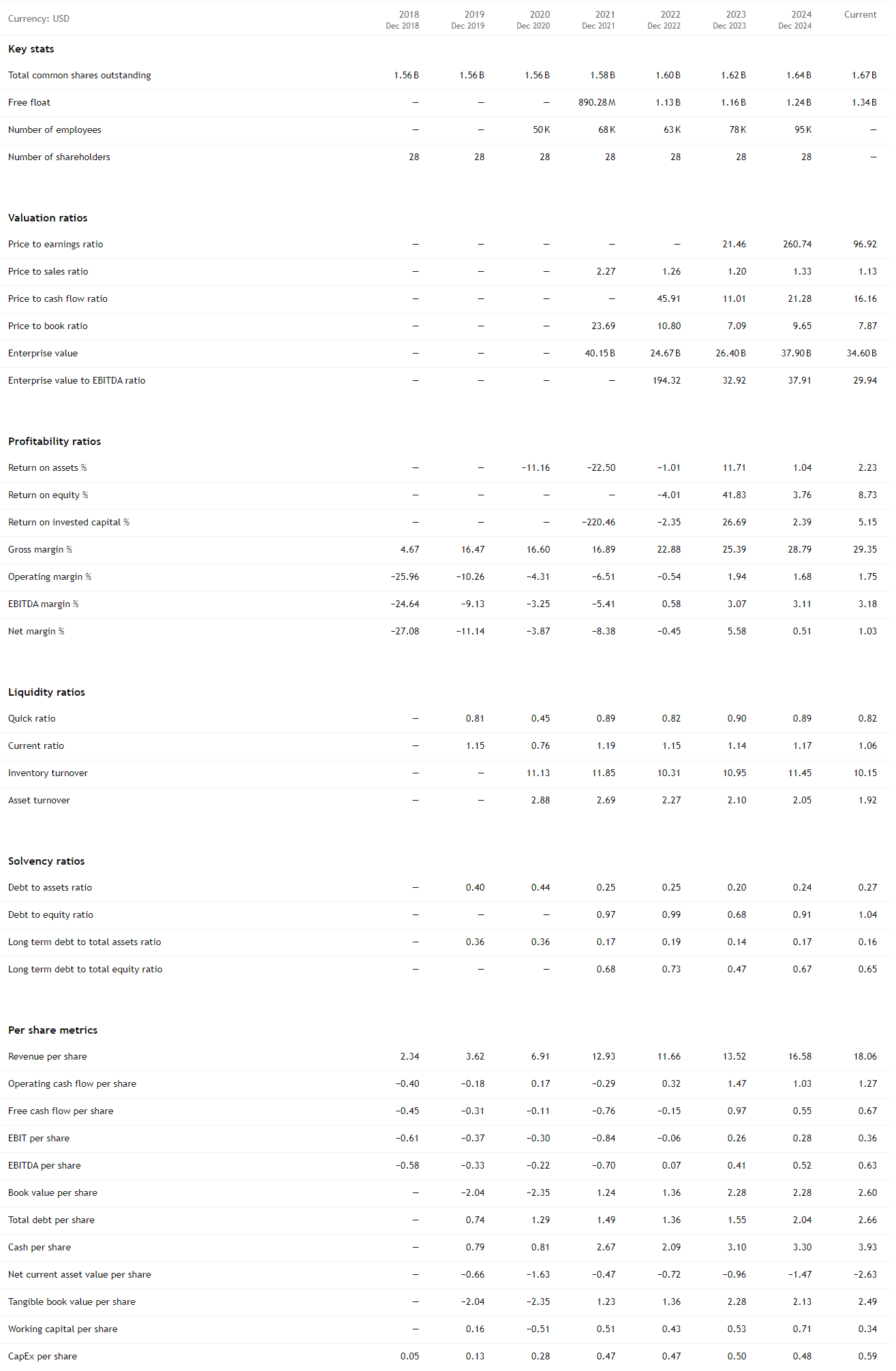
Statistics
Sources: Coupang
Unlock the power of compounding
We are changing the way that people build wealth. If your portfolio is performing below S&P 500 in the last 5 years, then you need to subscribe here. Discover remarkable stories directly to your inbox. As a subscriber, you'll receive the valuable recommendation of an exceptionally outstanding company that are designed to help you build wealth.
Gain access to exclusive benefits by subscribing today!






Disclaimer: Please note that this newsletter is a financial information publisher and not an
investment advisor. Subscribers should not view this newsletter as offering personalized legal or investment
counseling. Investors should consult with their investment advisor and review the prospectus or financial / stock
recommendation of the issuer in question before making any investment decisions. All articles, blogs, comments,
emails, and chatroom contributions - even those including the word "recommendation" - should never be construed as
official business recommendations or advice. Liability of all investment decisions resides with the individual
investor.
Snowball Investing does not provide any guarantees, warranties, or representations, whether explicitly or
implicitly, regarding the accuracy, reliability, completeness, or reasonableness of the information presented. The
opinions, assumptions, and estimates expressed represent the author's viewpoints as of the publication date and are
subject to modification without prior notification. Projections made within the document are based on various market
condition assumptions, and there is no assurance that the anticipated results will be attained. Snowball Investing
disclaims any responsibility for losses incurred due to reliance on this document's content. It is important to note
that Snowball Investing is not offering financial, legal, accounting, tax, or other professional advice, nor is it
assuming a fiduciary role.




Member discussion